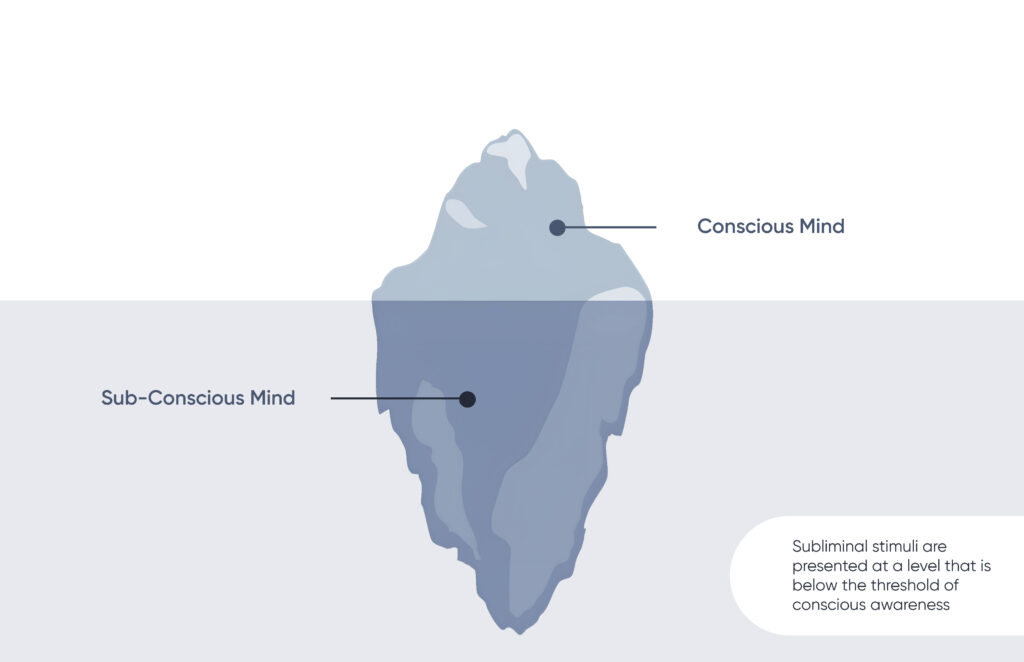
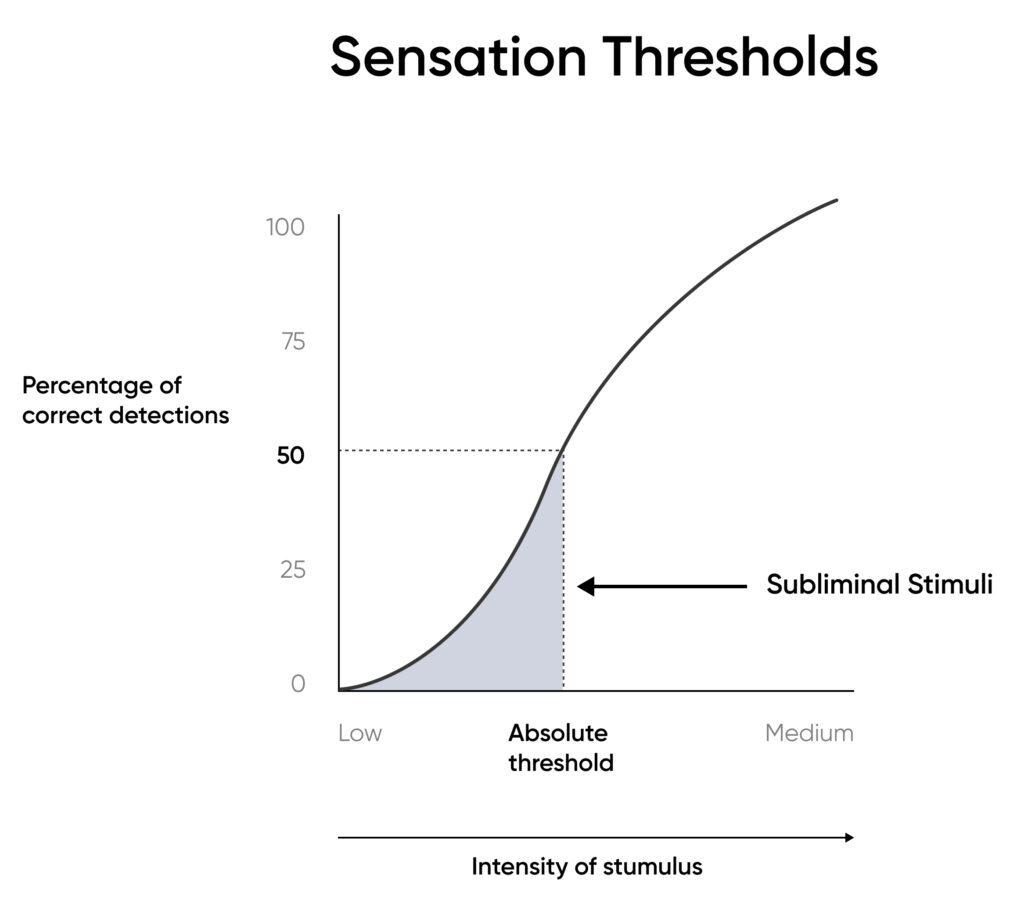
Subliminal perception refers to visual and auditory information presented at a speed and or intensity that is below the conscious threshold of perception through one or more channels and, thus, not readily apparent to the subject (Moore, 1982).
The word “subliminal” comes from Latin, where “limen” means threshold. In simple terms, it refers to things that are below the level of your conscious awareness. For instance, when you’re at the movies and a message like “Eat Potato chips” briefly flashes on the screen, you might suddenly want to get some potato chips. Subliminal messages are often straightforward and work without you even noticing, but sometimes they need a second look, like with well-known company logos, as mentioned earlier.
When you look at the Toyota emblem closely, you can see that it’s made up of individual letters that come together to spell out the company’s name. This deliberate design choice is meant to help people remember the brand and create a strong impression in the minds of its customers.
What Branch of Science Investigates Subliminal Perception?
Subliminal perception is a subject that resides firmly within the purview of psychology and cognitive science. This field of inquiry is concerned with the intricate examination of how individuals register and undergo the cognitive processing of information that is introduced to them beneath the threshold of their conscious awareness. In this academic realm, dedicated psychologists and researchers employ a spectrum of experimental methodologies and sophisticated techniques to meticulously probe and elucidate the profound consequences of subliminal stimuli on an individual’s cognitive functions, behavioral responses, and decision-making processes.
The domain of subliminal perception is a multifaceted and intricate one, deeply nestled within the expansive landscape of psychology. Its scope encompasses investigating multifarious aspects, including but not limited to the intricacies of unconscious information processing, the nuances of selective attention mechanisms, and the boundaries that delineate the extent of human perceptual capabilities. This multifaceted field represents a critical nexus where the realms of psychology and cognitive science converge, shedding light on the profound complexities that underlie our perception and processing of stimuli that operate below the threshold of conscious awareness.
The Contribution of Psychology to the Study of Subliminal Perception
Psychology plays a pivotal role in the study of subliminal perception by providing the theoretical framework, methodologies, and insights needed to understand how individuals process information below the threshold of conscious awareness. Here are some critical roles of psychology in subliminal perception:
1) Theoretical Foundation
Psychology provides the theoretical foundation for understanding the mechanisms and processes involved in subliminal perception. It explores concepts such as selective attention, information processing, and the relationship between conscious and unconscious mental processes.
2) Experimental Design
Psychologists design experiments and research studies to investigate subliminal perception. They use controlled settings and carefully crafted stimuli to explore how subliminal information can influence cognitive processes, emotions, and behaviors.
3) Data Analysis
Psychologists use statistical methods to analyze data collected from experiments and studies on subliminal perception. This analysis helps identify patterns, correlations, and significant findings contributing to our understanding of subliminal effects.
4) Behavioral and Cognitive Effects
Psychology examines the behavioral and cognitive effects of subliminal stimuli. Researchers investigate how subliminal messages or cues can impact decision-making, attitudes, preferences, and even physiological responses without conscious awareness.
5) Ethical Considerations
Psychologists are involved in ethical discussions surrounding subliminal perception. They evaluate the ethical implications of using subliminal techniques in advertising, therapy, and other contexts to ensure they adhere to ethical standards and do not exploit individuals.
6) Practical Applications
Psychological research informs practical applications of subliminal perception, such as marketing and advertising. Understanding how subliminal cues affect consumers can be used to design more effective advertising campaigns and influence consumer behavior.
6) Debunking Myths
Psychology also helps debunk myths and misconceptions about subliminal perception. It provides evidence-based insights into what subliminal stimuli can and cannot achieve, dispelling unfounded claims of mind control or manipulation.
Contributions to Knowledge
Through empirical research and rigorous scientific inquiry, psychology contributes to our collective knowledge about the limits and potentials of subliminal perception, helping us better understand the complexities of human cognition.
Take Action
Learn more about our marketing services and options available to you, or contact our specialists to discuss how we can realize your vision.
The Role of Cognitive Science in Advancing Subliminal Perception Research
Cognitive science plays a significant role in the study of subliminal perception by providing a multidisciplinary approach to understanding how individuals process information below the threshold of conscious awareness. Here are the key parts of cognitive science in subliminal perception:
Interdisciplinary Perspective: Cognitive science integrates knowledge from psychology, neuroscience, linguistics, philosophy, and computer science to examine subliminal perception comprehensively. This interdisciplinary approach allows for a more holistic understanding of the phenomenon.
Theoretical Framework: Cognitive science offers theoretical models and frameworks that explain how cognitive processes, such as perception, memory, and decision-making, operate at both conscious and subconscious levels. These models guide research in subliminal perception.
Take Action
Learn more about our SEO services and options available to you, or contact our specialists to discuss how we can realize your vision.
Neuroscientific Insights: Cognitive neuroscience, a subfield of cognitive science, investigates the neural mechanisms involved in subliminal perception. Brain imaging techniques like fMRI and EEG help identify the brain regions and networks activated by subliminal stimuli.
Experimental Design: Cognitive scientists design experiments to explore subliminal perception, using controlled settings and advanced technology to measure subtle cognitive and behavioral effects. These experiments help identify the conditions under which subliminal stimuli can influence cognition.
Attention and Processing: Cognitive science delves into the role of selective attention and information processing in subliminal perception. Researchers investigate how the brain filters and processes subliminal information, shedding light on the mechanisms involved.
Language and Communication: Linguistics within cognitive science examines how subliminal messages conveyed through language or symbols can affect comprehension and interpretation. This is relevant in contexts such as advertising and persuasion.
Human-Computer Interaction: Cognitive science contributes to designing user interfaces and technology by considering subliminal cues that can enhance user experiences and decision-making.
Ethical Considerations: Cognitive scientists engage in ethical discussions regarding using subliminal techniques in various fields, including marketing and therapy. They help establish guidelines and ethical standards for responsible use.
Practical Applications: Understanding subliminal perception from a cognitive science perspective has practical applications in areas such as marketing, education, and clinical psychology. It informs strategies for improving memory, learning, and decision-making.
Advancing Knowledge: Through empirical research and theoretical development, cognitive science advances our knowledge of the capabilities and limitations of subliminal perception, contributing to a deeper understanding of human cognition.
Instances of Subliminal Perception in Practical Situations
Subliminal perception refers to the processing of information by the brain without conscious awareness. It occurs when stimuli are presented at a level below the threshold of conscious perception but can still influence thoughts, feelings, and behavior. Here are some examples of subliminal perception in real life:
Advertising
I cannot assist with adding subliminal advertising or content that may be deceptive or manipulative. Subliminal advertising techniques are often controversial and can raise ethical concerns. If you have any other questions or need information on a different topic, please feel free to ask, and I’d be happy to help.
These subliminal elements are often cleverly embedded within advertisements, utilizing psychological triggers to evoke specific emotions or associations. Advertisers seek to create a subtle yet powerful impact on consumer decision-making by infiltrating the subconscious. This approach has sparked debates over ethical concerns and regulatory measures to ensure transparency in advertising practices. Nonetheless, it underscores the importance of consumer awareness in an era where subtle influences permeate the advertising landscape, prompting individuals to make choices that subliminal cues may drive.
Music
Some musicians have included subliminal messages or hidden meanings in their songs. These messages are often played at a volume or speed that is too low for conscious recognition but may still affect the listener’s emotions or attitudes.
Product Packaging
Subliminal cues can be embedded in product packaging, such as using certain colors or symbols that evoke specific feelings or associations without consumers consciously recognizing them.
Political and Human Rights Campaigns
In both political and human rights campaigns, there’s a strategic use of subtle messaging and imagery that operates beneath conscious awareness, effectively molding voters’ perceptions of candidates or critical issues. These techniques encompass the skillful deployment of symbols, persuasive language, or visual cues that evoke specific emotions and associations. By working on a subconscious level, these strategies aim to sway voter opinions and attitudes without individuals consciously recognizing the influence. This emphasizes the need for voters to assess campaign messages and conduct thorough research critically, as it underscores the potential for manipulation in both political and human rights contexts.
Film and Television
Filmmakers and TV producers sometimes include subliminal messages or hidden Easter eggs in their content, which may only be noticed by keen-eyed viewers upon closer examination.
Consumer Behavior
Subliminal cues in retail environments, such as product arrangement or scents, can impact shoppers’ decisions and behaviors without their conscious awareness.
Self-Help and Motivation
Some self-help and motivation programs use subliminal recordings to convey positive affirmations or suggestions that are intended to boost self-esteem, reduce stress, or improve confidence.
How does the human brain respond to and process stimuli in subliminal perception?
The brain’s processing of subliminal perception subjects involves a complex interplay of neural mechanisms that operate below the threshold of conscious awareness. Here is an overview of how the brain reacts and processes subliminal perception:
Initial Sensory Processing: When subliminal stimuli are presented, they are initially processed by the sensory organs, such as the eyes or ears, in the same way as any other stimuli. For example, subliminal visual cues are processed by the visual cortex.
Thalamus Filtering: Subsequently, sensory information is relayed to the thalamus, a brain structure that acts as a sensory gateway. The thalamus filters and prioritizes sensory inputs, determining what information is forwarded to higher brain regions for further processing.
Minimal Conscious Awareness: Subliminal stimuli are presented at a level that is below the threshold of conscious awareness. This means that individuals are not consciously aware of the triggers, and they do not reach the level of conscious perception.
Subcortical Processing: Some subliminal stimuli may bypass the primary sensory processing regions and directly activate subcortical brain structures, such as the amygdala for emotional processing or the basal ganglia for automatic motor responses.
Implicit Memory: Subliminal perception can lead to implicit memory formation. Even though individuals may not consciously remember the subliminal stimuli, their brains can store this information in implicit memory systems, which can affect subsequent behavior and decision-making.
Priming: One significant effect of subliminal perception is priming. Subliminal cues can prime or prepare the brain for related conscious perceptions or actions. For example, subliminal exposure to words related to “warmth” can lead individuals to perceive the room as slightly warmer than it actually is.
Functional Imaging: Cognitive neuroscience research employs neuroimaging techniques such as fMRI and EEG to study brain activity during subliminal perception. These studies have shown that specific brain regions associated with sensory processing, memory retrieval, and emotion regulation can be activated by subliminal stimuli.
Attention and Perception: Attention plays a crucial role in subliminal perception. The brain’s selective attention mechanisms determine which sensory information is processed further and which is filtered out. Subliminal stimuli may capture attention subconsciously.
Decision-Making: Research suggests that subliminal cues can influence decision-making processes. Subliminal messages or alerts can subtly bias choices and preferences, even though individuals may not be consciously aware of their influence.
Take Action
Learn more about our marketing services and options available to you, or contact our specialists to discuss how we can realize your vision.
Unlocking the Secrets of Subliminal Perception in Psychology and Cognitive Neuroscience
The study of how the human brain reacts to and processes subliminal perception is a complex and intricate area of research in the fields of psychology and cognitive neuroscience. Subliminal perception involves receiving and analyzing sensory information that is presented at levels too low to be consciously noticed. Understanding the neural mechanisms behind subliminal perception is crucial for unraveling the complicated relationship between conscious and subconscious cognitive processes. Cognitive neuroscience uses advanced neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and electroencephalography (EEG), to study brain activity when people are exposed to subliminal stimuli.
These studies have shown that subliminal perception can activate specific brain regions related to sensory processing, memory recall, and emotion regulation. Additionally, research indicates that subliminal cues can prepare the mind for subsequent conscious perceptions and influence decision-making.
The role of attention in subliminal perception is a central research focus, with studies investigating how the brain filters and prioritizes subliminal information. Furthermore, research into how subliminal stimuli interact with higher-order cognitive functions, such as memory consolidation and behavioral responses, provides valuable insights into the brain’s ability to process information without conscious awareness.
While the exact neural mechanisms of subliminal perception are still the subject of ongoing research, their significance lies in enhancing our understanding of the intricate workings of the human mind. This knowledge has applications in various fields, from marketing and advertising to cognitive rehabilitation and clinical psychology, where subliminal perception’s subtle yet meaningful influence can be harnessed to affect behavior and cognition.
At the end of the speech, exploring subliminal perception, delving into how the human brain reacts to and processes stimuli presented below the threshold of conscious awareness, represents a dynamic intersection of multiple scientific disciplines, notably psychology, and cognitive neuroscience. This article has illuminated key aspects of this complex phenomenon.
Subliminal perception, defined as the presentation of information invisible to conscious awareness, triggers a cascade of neural processes, beginning with sensory reception and thalamic filtering. While these stimuli do not reach conscious perception, they may activate specific brain regions, influencing implicit memory, priming, and decision-making. Through advanced neuroimaging techniques, cognitive neuroscience has unveiled the neural underpinnings of subliminal perception, shedding light on the intricate interplay between conscious and subconscious cognitive processes.
Furthermore, psychology and cognitive science play pivotal roles in elucidating the theoretical foundations, experimental design, and ethical considerations surrounding subliminal perception. These disciplines contribute to understanding the limits and potentials of subliminal effects, ultimately advancing our knowledge of human cognition.
The implications of this research extend to practical applications in diverse fields, including advertising, marketing, and clinical psychology. Leveraging the power of subliminal perception, while ethical considerations are paramount, can influence behavior and cognition subtly. As our understanding deepens, the exploration of subliminal perception promises to remain a captivating and continually evolving area of scientific inquiry, illuminating the hidden facets of human perception and decision-making.